Cells are the basic units of life, yet not all cells are the same. Living organisms are divided into two major groups based on their cell structure: prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Understanding the similarities and differences between them is a fundamental concept in biology. In this article, we’ll compare their structures, functions, and evolutionary importance in a way that is simple, yet in-depth enough to satisfy advanced learners.
What Are Prokaryotes?
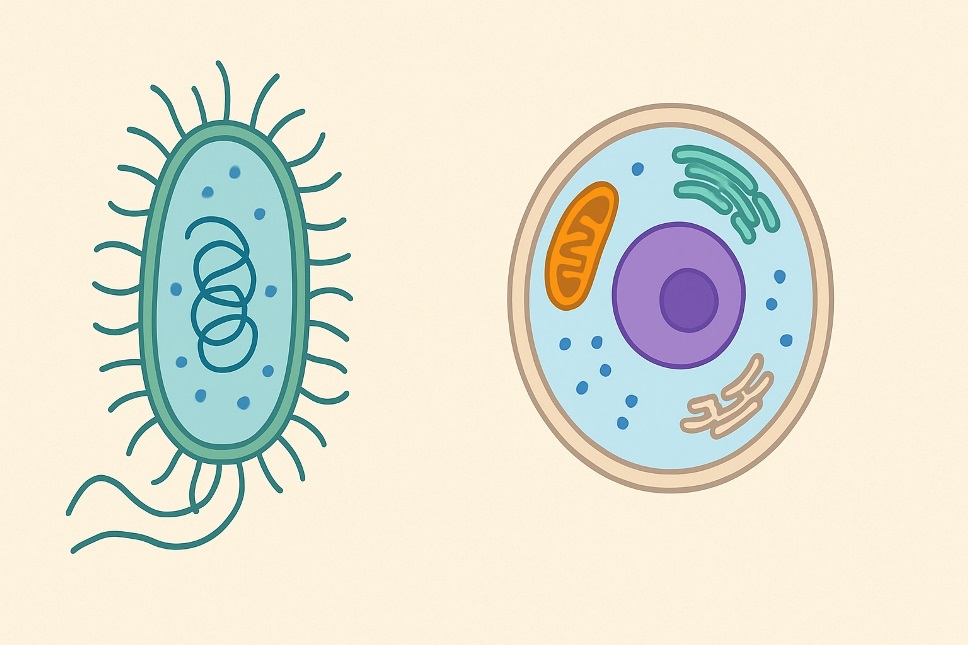
Prokaryotes are the simplest and most ancient form of life. They are unicellular organisms that lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Instead, their genetic material is found in a single circular DNA molecule located in a region called the nucleoid.
The most common examples of prokaryotic organisms are bacteria and archaea. These organisms thrive in diverse environments, ranging from soil and water to extreme habitats like hot springs and salt flats. Their small size, usually between 0.1 and 5 micrometers, gives them the ability to reproduce rapidly through a process called binary fission.
What Are Eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes are more complex cells that evolved later in Earth’s history. Unlike prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane. They also contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts (in plants), endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus.
Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers, and are the building blocks of multicellular organisms, including animals, plants, fungi, and protists. They reproduce through mitosis or meiosis, processes that allow genetic variation and complexity.
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: Key Differences

The primary difference between these two cell types lies in their structural complexity. Below is a breakdown of major distinctions:
- Nucleus: Prokaryotes lack a nucleus; eukaryotes have one.
- DNA: Prokaryotic DNA is circular, while eukaryotic DNA is linear and arranged into chromosomes.
- Organelles: Only eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles.
- Cell Division: Prokaryotes divide by binary fission, while eukaryotes undergo mitosis or meiosis.
- Size: Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler; eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex.
These differences shape the way each cell functions and adapts to its environment.
Similarities Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes

Despite their differences, both cell types share some fundamental characteristics:
- Both contain DNA as their genetic material.
- Both have ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Both are surrounded by a plasma membrane that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Both carry out essential life processes such as metabolism, growth, and response to stimuli.
This common ground highlights their shared evolutionary origins.
Evolutionary Perspective
Prokaryotes appeared on Earth around 3.5 billion years ago, long before eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved from prokaryotic ancestors through a process called endosymbiosis, where one prokaryotic cell engulfed another, leading to the development of organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
This theory explains why mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and resemble bacteria in structure. The evolution of eukaryotic cells allowed for greater cellular complexity, paving the way for multicellular organisms and biodiversity.
Also Read: HCOOCH CH2 H2O: Essential Chemical Properties You Should Know
Examples of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Organisms

- Prokaryotic Examples: Escherichia coli (E. coli), Staphylococcus aureus, and Methanogens.
- Eukaryotic Examples: Humans, oak trees, yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), and amoebas.
These examples show how each cell type contributes to life on Earth in different ways.
Why the Comparison Matters
Understanding the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is essential in multiple fields:
- Medicine: Many antibiotics specifically target features unique to prokaryotic cells, like bacterial ribosomes.
- Biotechnology: Prokaryotes are used in genetic engineering, while eukaryotes are essential for protein production in labs.
- Ecology: Both types play key roles in ecosystems, from nutrient cycling by bacteria to energy flow in plants and animals.
This knowledge bridges basic biology with applied sciences.
Incorporation of Essential Keywords
To ensure clarity and SEO optimization, here are the required keyword phrases used naturally in context:
- Scientists often study prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells to understand evolutionary complexity.
- The term prokaryotes vs eukaryotes is central in biology textbooks for classifying life.
- Many students confuse eukaryotic vs prokaryotic structures when learning cell biology.
- Comparing a prokaryote vs eukaryote highlights the importance of organelles in life processes.
- Classroom discussions frequently focus on eukaryotes vs prokaryotes to explain diversity of life forms.
Conclusion
The comparison of prokaryotes and eukaryotes reveals how life ranges from the simplest single-celled organisms to highly complex multicellular beings. While prokaryotes showcase efficiency and adaptability in simplicity, eukaryotes demonstrate how complexity allows for advanced functions and diversity. Both are essential for the survival and progression of life on Earth.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The main difference is that prokaryotes lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes have both.
2. Which type of cell is older, prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic cells are older, appearing about 3.5 billion years ago, whereas eukaryotic cells evolved around 2 billion years ago.
3. Do both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have DNA?
Yes, both types of cells contain DNA as their genetic material, though its structure and location differ.
4. Why are prokaryotes important to humans?
Prokaryotes play key roles in digestion, nutrient cycling, and biotechnology, but some can also cause disease.
5. How did eukaryotic cells evolve from prokaryotes?
Eukaryotic cells are thought to have evolved through endosymbiosis, where one prokaryotic cell engulfed another, leading to the origin of organelles like mitochondria.